Excessive Menstrual Bleeding
If your menstrual periods are so heavy that they affect your normal activities, you may have excessive menstrual bleeding. The medical term for periods that are very heavy, last longer than normal or both is menorrhagia. Symptoms may also include cramping, pelvic pain and anemia.
Excessive menstrual bleeding is a common condition that occurs for many reasons. Two of the most common causes are a hormone imbalance and uterine growths.
Hormone Imbalances
Your menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. When these hormones are out of balance, they can cause heavy periods or bleeding between periods. Causes of hormonal imbalances may include:
- Hormone changes in teens and in women nearing menopause
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disease
- Obesity
- Stress
- Strenuous exercise
- Anorexia (eating disorder)
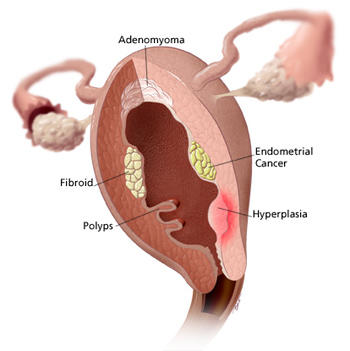
Types of Uterine Growths
- Fibroids – benign (non-cancerous) growths in or near the uterus
- Polyps – growths that attach to the inner wall of the uterus and protrude into the uterine cavity
- Adenomyosis – endometrial tissue normally lining the uterus grows into the muscular walls of the uterus
- Endometriosis – tissue that normally lines the inside of your uterus grows outside your uterus
- Endometrial cancer – an uncontrolled growth of cells in the uterine lining
- Hyperplasia – an abnormal proliferation of cells (cell division or growth) that may result in enlargement (growth) of the uterus. This term is sometimes used to refer to a benign tumor or fibroid.