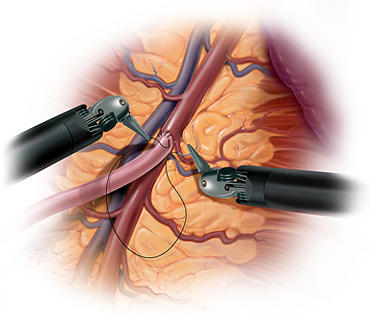
ROBOTIC SURGERY – or robot-assisted surgery is a minimally invasive surgery whereby the surgeon utilizes robotic systems & platforms to allow them to perform complex procedures with more precision, accuracy and control than conventional open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. The surgical robots were designed to enhance the capabilities of open surgery such as the large incisions increasing the chances for post-op pain, wound infection & bleeding, while overcoming the limitations of laparoscopic surgery such as reverse orientation, surgeon fatigue, straight instruments with absence of rotational movements. The Da Vinci Robot was FDA approved for gynecologic surgery in 2005. Robotic surgery can be performed as an outpatient procedure or an overnight procedure, if uncomplicated. Like laparoscopic surgery, it is also a minimally invasive surgery that utilizes tiny incisions or band-aid incisions (since they are small enough to be covered with a Band-Aid). However, it is a more enabling tool, since the instruments have jointed wrist that allow it to have 7 degrees of freedom, more than the human hand and therefore seamlessly and effectively translate the surgeon’s hand movements into the more precise movements of the instrument tips. It eliminates the fulcrum effect leading to reverse orientation inherent to laparoscopic surgery. In contrast to the reverse orientation when doing laparoscopic surgery, the movements in robotic surgery are all intuitive and because the instruments rotate, it is a much easier tool for especially for suturing the defects left when removing a myoma from the uterine wall, or when suturing the vaginal stump to close it after hysterectomy.
In performing laparoscopy, usually the distance of the tissue structure from the port site on the abdomen causes amplification of motion at the instrument tip. This means that a surgeon’s tiny movement with the instruments outside the body causes a relatively large motion on the inside as seen by the camera on the monitor. This can make targeting tissues difficult and frustrating and requires a learning curve to overcome. With the daVinci Surgical Robot, motions are filtered and de-amplified up to a scale of 5 to 1. In other words, the surgeon would have to move the manipulators up to 5 inches in order to cause movement of only an inch on the inside of the body. This is even adjustable to a 3:1 ratio, meaning for every three inches of movement of the surgeon, the machine scales this down to 1 inch of movement of the instruments. This eliminates natural hand tremor entirely, allows the surgeon to target tissues with much greater ease, and gives the surgeon a certain accuracy and refinement that surpasses human capabilities for both the open and standard laparoscopic paradigms.
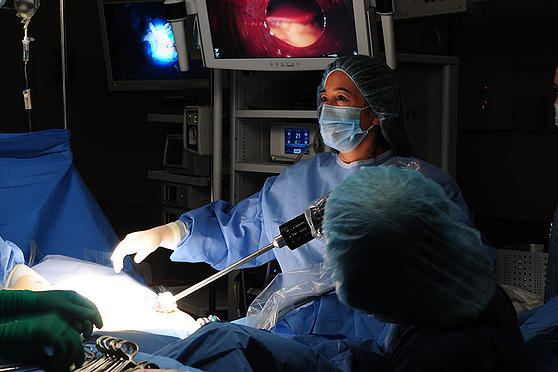
Dra. Rebecca Singson performing a robot assisted surgery.
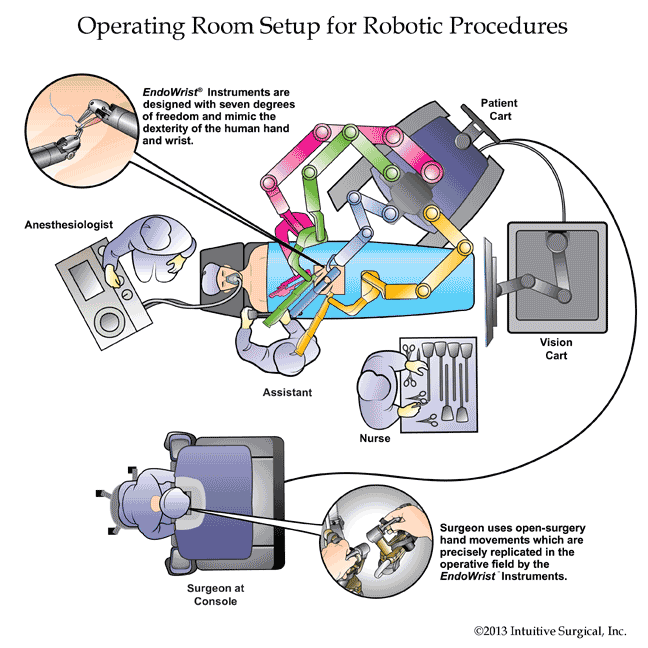
Ergonomics is another realm of superiority for the Da Vinci robot. With traditional laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon is standing on the operating table and awkwardly struggling to move the straight instruments manually while keeping the head fixed on the monitor to visualize the movements inside the abdomen. With the Da Vinci robot, the surgeon ergonomically sits on the surgeon’s console, which memorizes the settings for every surgeon. The head is positioned with minimal strain to the neck while looking into the 3-dimensional vision system (laparoscopy only has a 2-diminsional vision system since it has only one camera whereas the robotic camera has 2 cameras: one for the left and another for the right eye). The arms are positioned to the perfect height preferred by the surgeon and the foot pedals are also adjusted to the preference of the surgeon. The vision system allows depth perception because of the 3-dimensional design and the ergonomic set up of performing surgery while seated on the surgeon’s console all translates to eliminating fatigue, especially for complicated surgeries that go on for several hours.